As 2023 draws to a close, we review this year’s published papers in a series of studies undertaken on thoroughbred cadaver limbs using Vision CT, fan beam CT, and MRI.
Sagittal and parasaggital grove fissures:
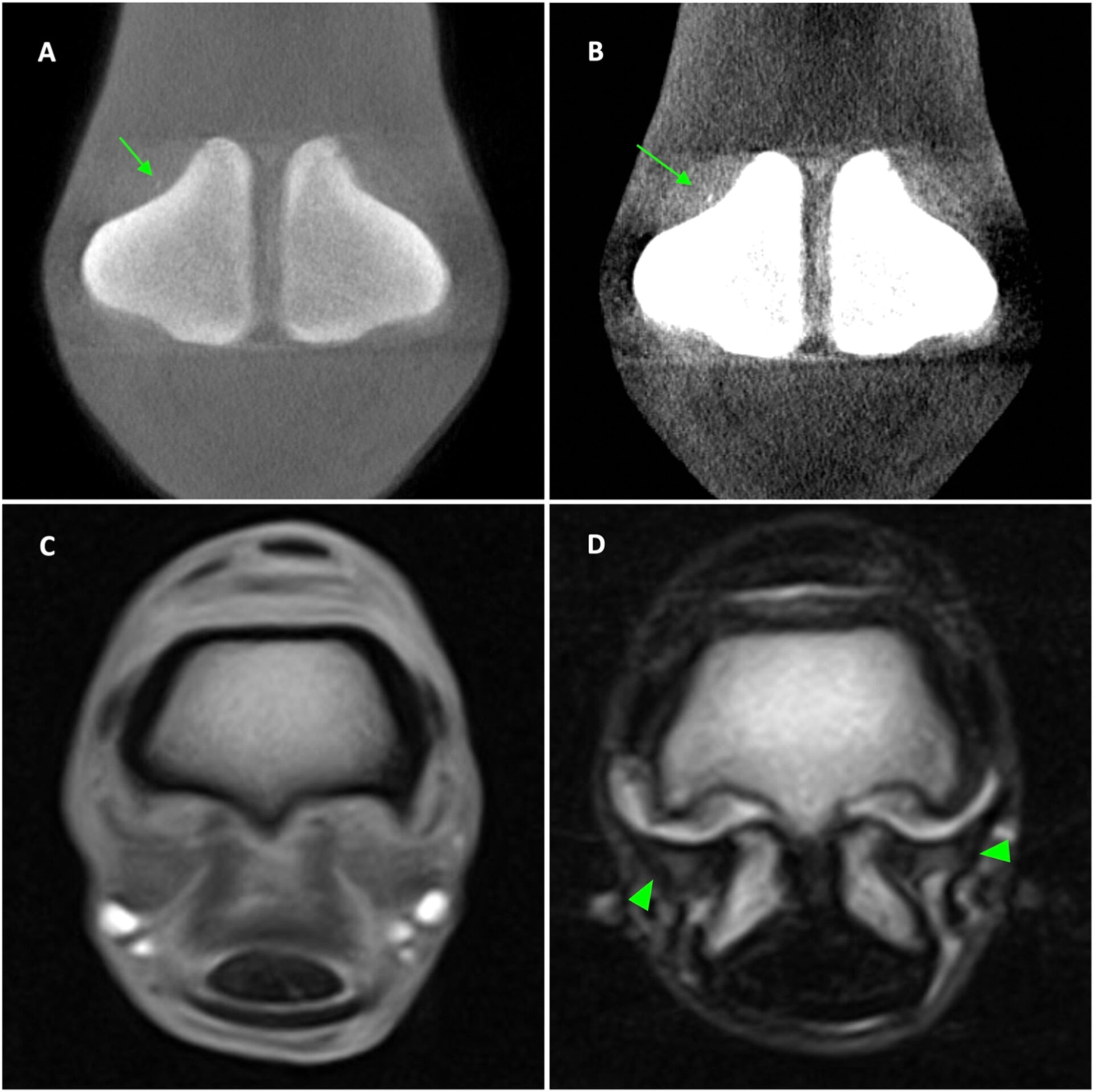
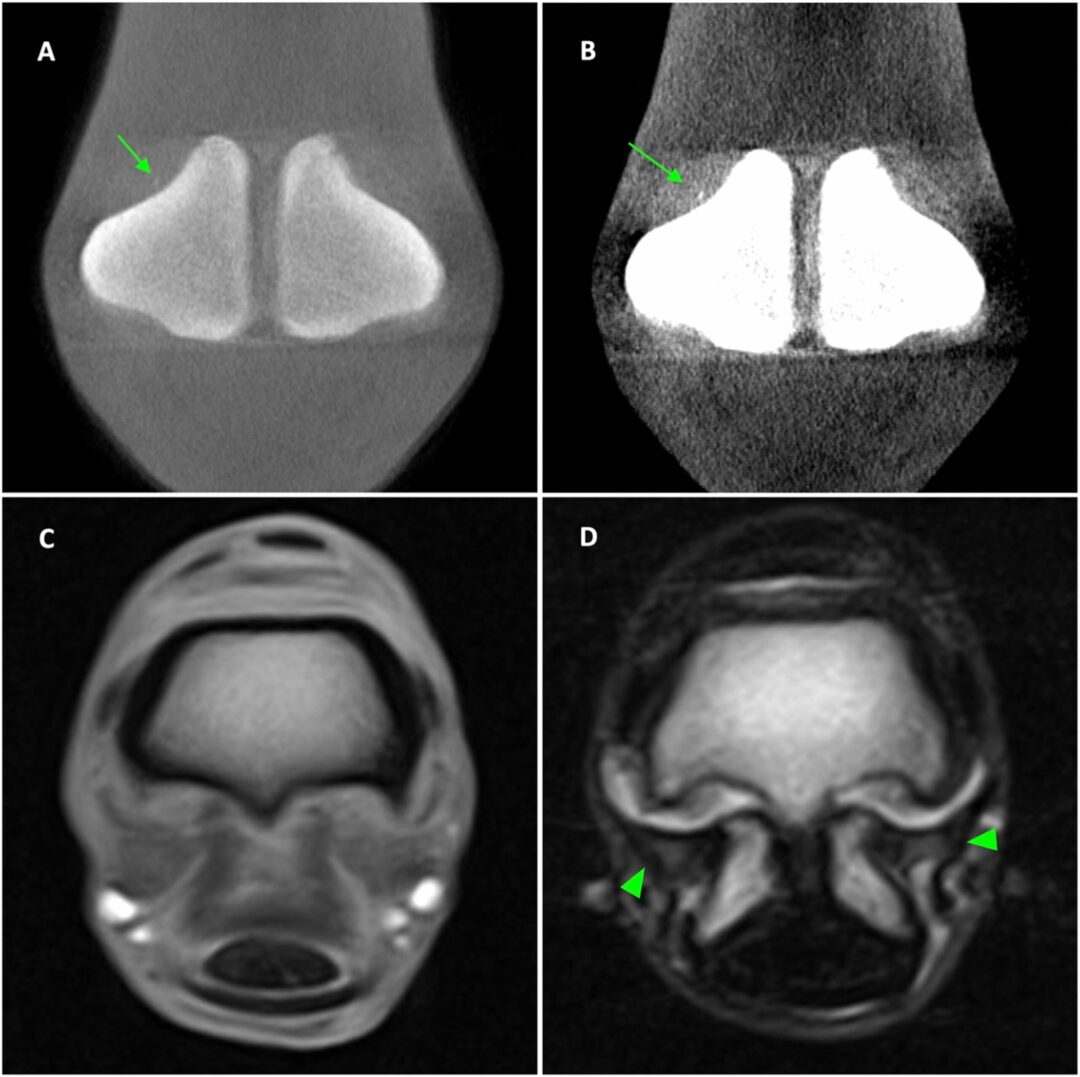
Fractures of the third metacarpal/tarsal parasagittal groove and proximal phalanx sagittal groove are common in racehorses. It is important to detect precursor pathologies including fissures to prevent the propagation to fracture. This study aims to identify the imaging features and compare the diagnosis of fissures on cone-beam (CB) computed tomography (CT), fan-beam (FB) CT, and low-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to histopathology associated with fissures.
Palmar osteochondral disease:
Palmar/plantar osteochondral disease (POD), also reported as traumatic osteochondrosis, subchondral bone injury (SBI), or focal palmar necrosis (FPN), is a common pathology affecting the palmar/plantar aspect of the metacarpal/tarsal condyles in racehorses. The study compares diagnoses, imaging details, and measurements of POD lesions between cone-beam computed tomography CT (CBCT), fan-beam CT (FBCT), and low-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using macroscopic pathology as a gold standard.
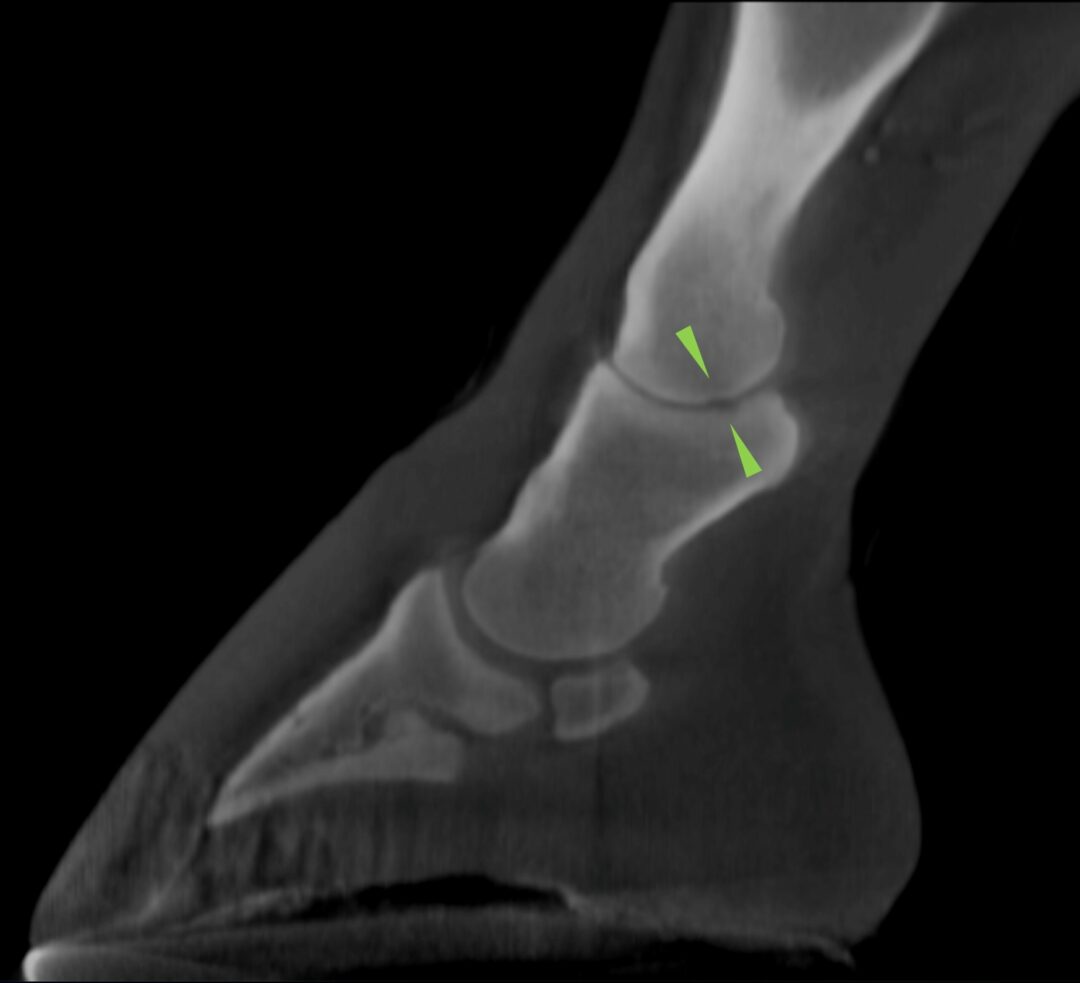
Proximal phalanx dorsoproximal osteochondral defects:
Osteochondral defects in the dorsoproximal aspect of the proximal phalanx, including the dorsomedial and dorsolateral eminences, are a common pathology affecting the metacarpophalangeal/metatarsophalangeal (fetlock) joint in horses. It is accepted that osteochondral defects can be related to developmental orthopaedic problems, or result from single or repetitive traumatic injuries during joint hyperextension, when the dorsoproximal aspect of the proximal phalanx is in contact with the dorsal aspect of the third metacarpal/metatarsal bone
Heterotopic mineralisation:
Computed tomography (CT) is recognized as the optimal imaging modality for detecting tendon and ligament mineralization and bone architectural alterations. By comparison, MRI is generally considered optimal for the evaluation of soft tissue injury and fluid-based bone injury. The practicality of CT imaging was once limited by the procedure of general anesthesia for image acquisition. However, recent advances have led to the development of standing CT technology for equine distal limb imaging in standing, sedated horses providing an opportunity to identify soft tissue mineralization in equine distal limbs more effectively.
INTERESTED IN VISIONARY VETERINARY IMAGING?