Contrast arthrogram of distal interphalangeal joint
The patient
In this case study, kindly provided by Valley Equine Hospital (VEH), we examine a horse with marked right forelimb lameness. An MRI scan of the affected limb revealed extensive bone oedema in the distal and middle phalanges. However, these findings did not fully correspond with the clinical presentation. Consequently, the horse was referred to VEH for Imaging with Hallmarq’s Vision CT to obtain additional diagnostic information.
CT findings
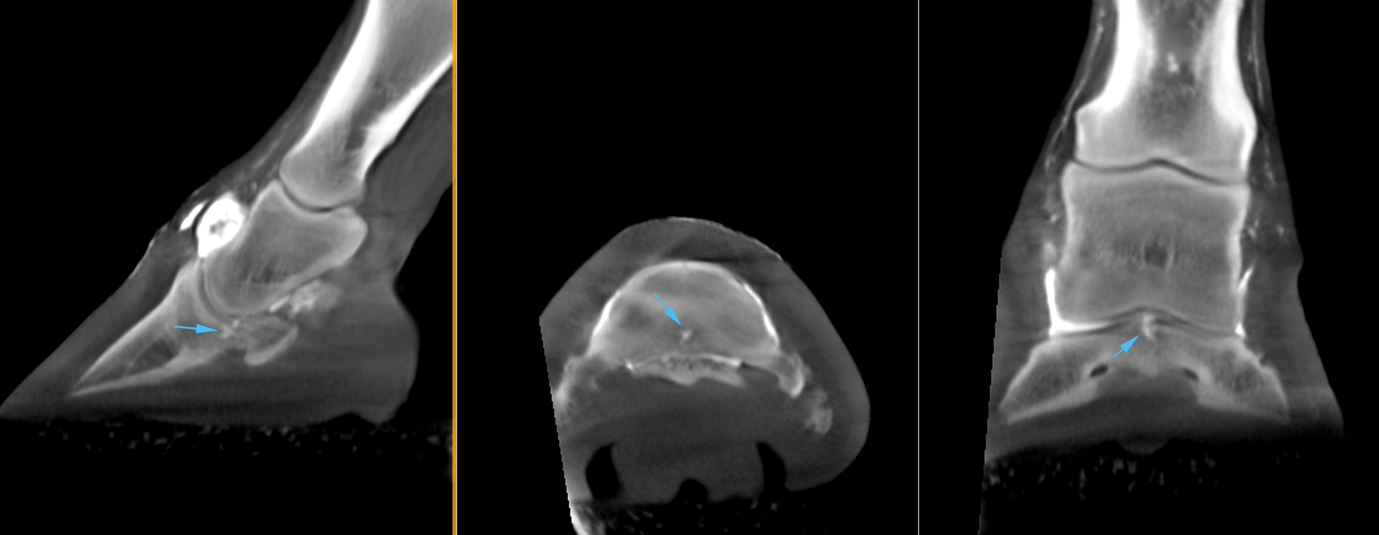
The main finding was a small focal irregularity in the palmar axial portion of the articular surface of the distal phalanx. An irregularly outlined osteochondral fragment was suspected. The surrounding bone was considerably less dense than the normal subchondral bone of this location, and this more lucent radiodensity extended distally into the trabecular bone of the distal phalanx. The region of suspected osteochondral fragmentation was slightly displaced proximally, disrupting the normal contour of the articular surface.

CT contrast study findings
A contrast material was present within the region of suspected osteochondral fragmentation in the palmar axial portion of the distal phalanx. The contrast extended in depth of approximately 5mm into the distal phalanx confirming the suspicion that there was a full-thickness lesion to the articular surface.

With thanks to Dr Tom McParland BVetMed DiplACVS (LA) MRCVS and Melissa Lockwood RVN, Valley Equine Hospital, UK, for sharing this case with us.